Google Tag Manager is a tag management system that lets you configure and instantly deploy tags on your website or mobile app from a web-based interface1.
What’s a tag?
Cite
Tags are segments of code provided by analytics, marketing, and support vendors to help you integrate their products into your websites or mobile apps.
…you configure and publish tags and how they fire from within the Tag Manager user interface.2
Three main concepts in GTM:
- events: user actions
- tags:
- external calls you want to make at a point of time;
- can include an event param
- triggers: the conditions when GTM will fire a tag
Web
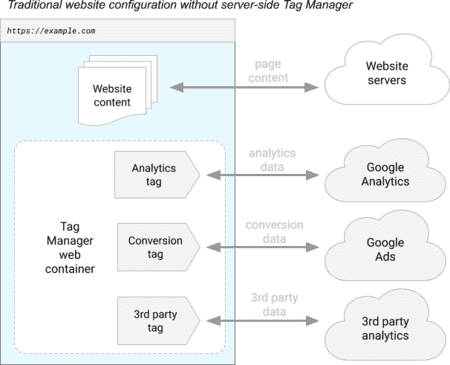
In web client scenarios, a tag could be advertising tracking pixels or full analytics SDK’s, which are JavaScript code that are injected to web pages at load time.
Cite
Google Tag Manager will allow the triggering of various third-party tracers (on the diagram: Google Analytics, Google Ads, and an analytics tool), directly on your browser4.
It’s a browser tool and requires an active browser session where JavaScript is downloaded and executed5. Another way to look at it is that this is basically a JavaScript injector - the Interface is there to configure your tags, then everything is wrapped into a JavaScript function that is inserted into your page and executed by the browser. There is no server-side component that you could push data to6.
To use GTM, you push events to the data layer:
dataLayer.push({
event: "transaction",
something: {
superSecret: 42,
},
})GTM will watch for the events and fire the corresponding tags based on the defined triggers.
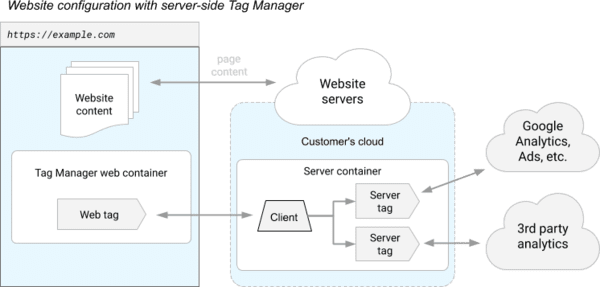
Server-side Tagging (SST)
Cite
The javascript library (called “Tag Manager web container” in the diagram) is always run on your browser in order to collect your interactions and your personal data, but the execution of the various third-party tracers takes place on the server side4.
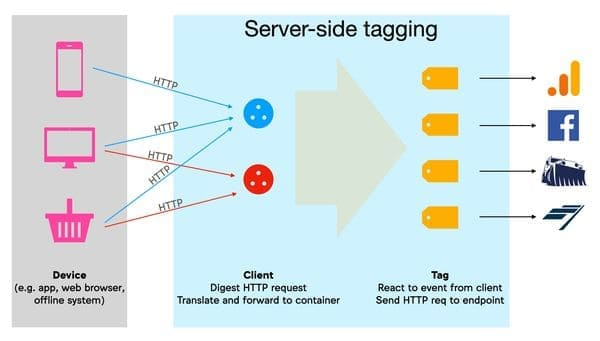
> on the server side, the "Clients" are there to translate the HTTP requests received into "events", the "Tags" react to these events to send "hits" to third-party marketing companies.
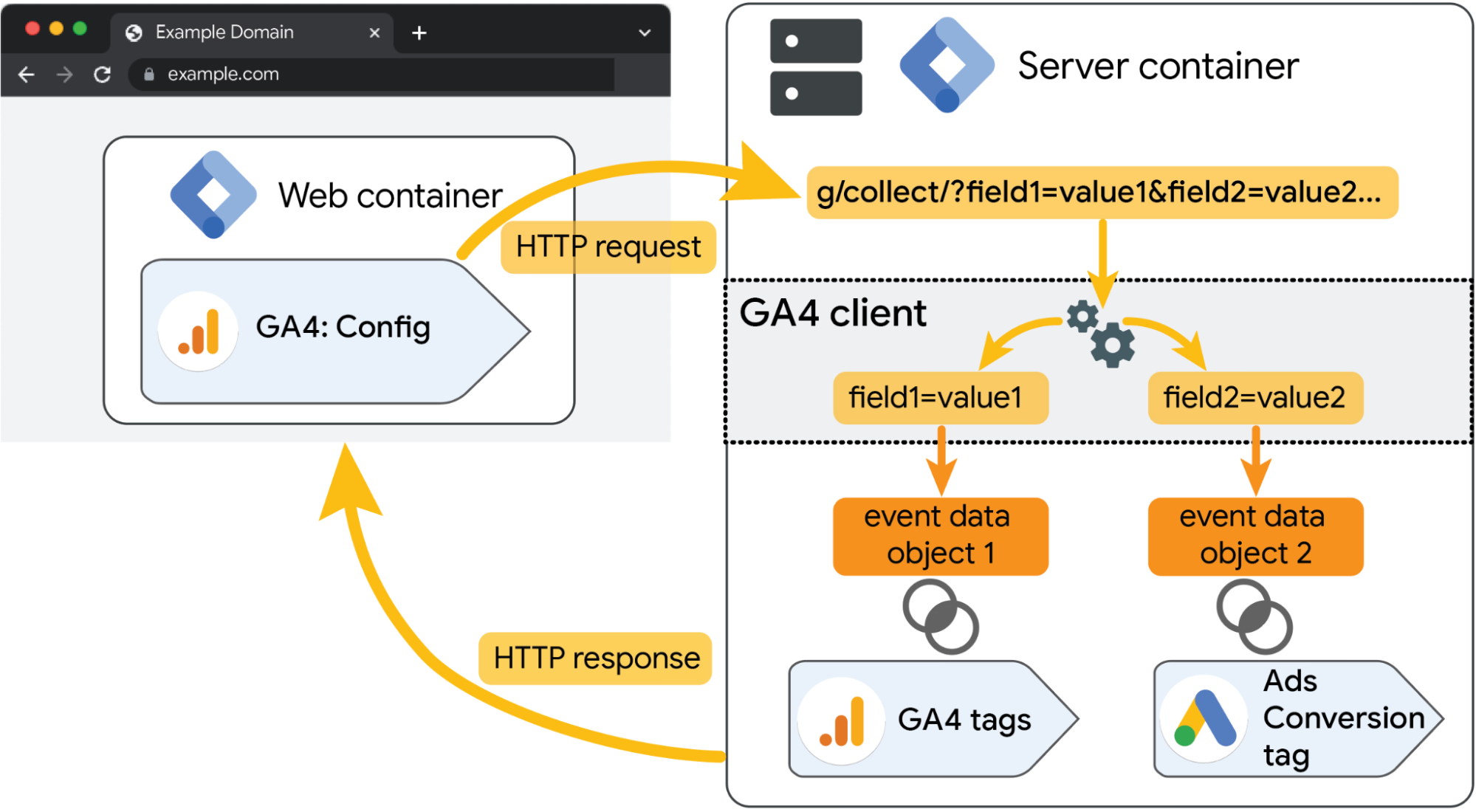 The server is a JavaScript application that runs in a server environment on Node.js. It’s packaged and distributed as a Docker image. It’s still recommended to use the client-side GTM to collect data, and then dispatch to the server-side tagging server environment. The server container does have endpoints that you can directly send requests to from our clients.
The server is a JavaScript application that runs in a server environment on Node.js. It’s packaged and distributed as a Docker image. It’s still recommended to use the client-side GTM to collect data, and then dispatch to the server-side tagging server environment. The server container does have endpoints that you can directly send requests to from our clients.
The goal of SST is more control, for:
- privacy
- performance
- data quality
Native Mobile
In native mobile client scenarios, GTM for Mobile uses event forwarding via Firebase Analytics to send events to the “tags”. Containers for Mobile cannot be shared with containers for Web.
Footnotes
-
https://developers.google.com/tag-platform/tag-manager “About Google Tag Manager” ↩
-
https://support.google.com/tagmanager/answer/6103696#zippy=%2Cwhat-is-a-tag “Set up and install Tag Manager” ↩
-
https://developers.google.com/tag-platform/tag-manager/server-side/intro “An introduction to server-side tagging” ↩ ↩2
-
https://chromium.woolyss.com/f/HTML-Google-Tag-Manager-the-new-anti-adblock-weapon.html “Google Tag Manager, the new anti-adblock weapon” ↩ ↩2
-
https://support.google.com/tagmanager/thread/15995701?hl=en&msgid=16762959 “Is it possible to fire tags from server-side code?” ↩
-
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/39774009/send-info-to-google-tag-manager-from-backend “Send info to google tag manager from backend” ↩
-
https://www.simoahava.com/analytics/server-side-tagging-google-tag-manager/ “SERVER-SIDE TAGGING IN GOOGLE TAG MANAGER” ↩